Key Takeaways
- In 2023, substance use disorder (SUD) impacted individuals of all ages, though rates varied significantly.
- Young adults, notably those aged 18–29, experienced the highest prevalence of SUD.
- Tailored approaches to prevention and treatment are essential to addressing this widespread issue.
Introduction
Substance use disorder (SUD) can affect anyone, regardless of age, background, or circumstances. However, the prevalence of SUD varies across different age groups, shaped by factors like life stage, stressors, and access to substances. Understanding these trends allows healthcare providers and policymakers to craft more effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Using data from the 2023 Substance Use Disorder by Age Group infographic, this article explores how SUD affects individuals at various stages of life, from teenagers to older adults. By diving into these age-specific patterns, we highlight where support is needed most and how recovery is achievable at any age.
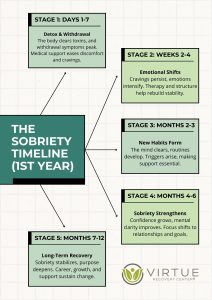
Teens (Ages 12–17): The Early Stage
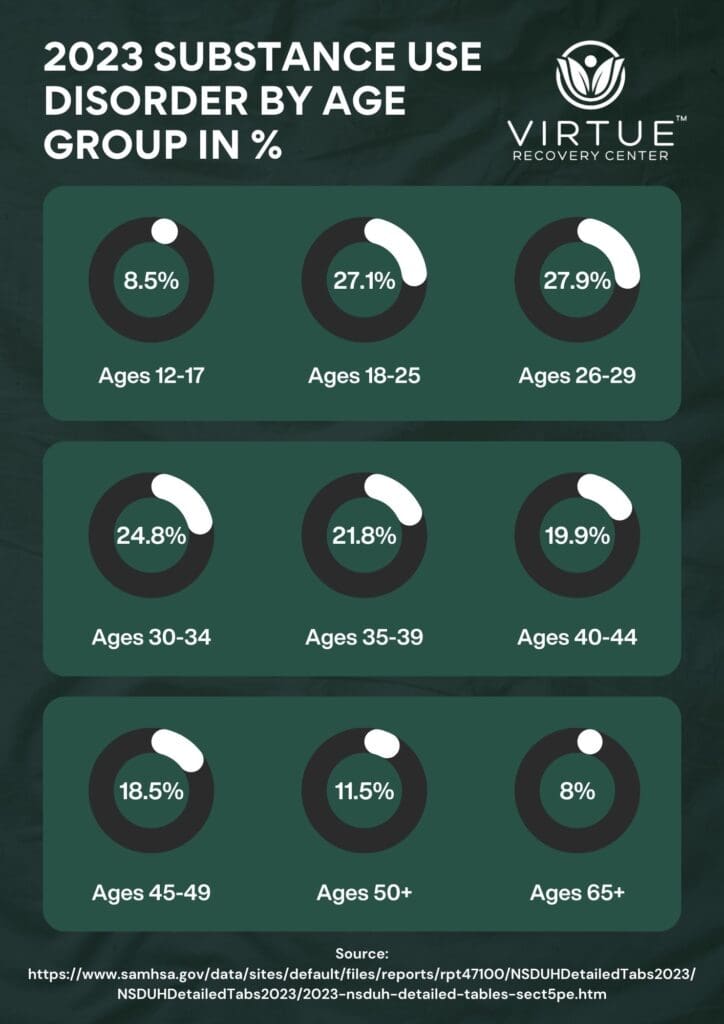
In 2023, 8.5% of teens aged 12–17 reported struggling with SUD. While this is the lowest prevalence across all age groups, it remains a critical issue, as early exposure to drugs or alcohol can set the stage for lifelong struggles with addiction.
Teenagers are particularly vulnerable to peer pressure and social influences, which can encourage experimentation with alcohol or marijuana. Additionally, stress from school or family problems may push some teens toward substance use as a coping mechanism. Addressing these issues early through educational programs, supportive family environments, and school-based interventions can significantly reduce the risk of SUD developing into adulthood.
Young Adults (Ages 18–29): The Most Affected
Young adults aged 18–29 represent the group most affected by substance use disorder. In 2023, 27.1% of those aged 18–25 and 27.9% aged 26–29 reported SUD, the highest rates among all age groups.
This stage of life is often marked by significant transitions, including entering the workforce, pursuing higher education, or establishing independence. These pressures, combined with a greater likelihood of socializing in environments where drugs or alcohol are present, make young adults particularly susceptible to substance use. Alcohol and marijuana are the most commonly used substances in this group, though misuse of prescription stimulants and opioids has also been on the rise.
The consequences of SUD during this period can be severe. Without proper intervention, young adults may face long-term health problems, difficulties maintaining employment, and strained personal relationships. Comprehensive treatment programs that focus on both the physical and psychological aspects of addiction are essential for supporting recovery in this age group.
Adults (Ages 30–49): Balancing Life Challenges
As individuals enter their 30s and 40s, the prevalence of SUD begins to decline but remains significant. In 2023, 24.8% of adults aged 30–34, 21.8% aged 35–39, and 19.9% aged 40–44 reported SUD.
At this stage of life, people often juggle demanding careers, family responsibilities, and financial pressures. These stressors can sometimes lead to substance use as a means of coping. Alcohol remains the most common substance used in this demographic, though opioid misuse has also been a growing concern.
For adults in this age range, SUD can have a profound impact on their families, especially their children. Parental substance use often creates a ripple effect, influencing the well-being of the entire household. Treatment programs designed for this age group frequently address these dynamics, offering family therapy and tools to rebuild relationships.
Older Adults (50+): An Overlooked Population
Although older adults have the lowest reported prevalence of substance use disorder, they face unique challenges that often go unnoticed. In 2023, 18.5% of individuals aged 45–49, 11.5% of those aged 50+, and 8% of those aged 65+ reported SUD.
Alcohol and prescription medications are the most commonly misused substances in this population. Chronic pain, mental health issues like depression, and social isolation are significant contributors to substance use among older adults. Additionally, stigma and the misconception that addiction only affects younger people may prevent seniors from seeking the help they need.
Specialized treatment programs for older adults are essential to addressing their unique needs. These programs often focus on managing chronic health conditions while providing emotional support in a nonjudgmental environment.
Insights from the 2023 Data About Drug and Alcohol Addiction
The 2023 Substance Use Disorder by Age Group infographic highlights critical trends that can guide public health efforts. Young adults are disproportionately affected, with rates nearing 28%. On the other hand, while older adults have lower prevalence rates, they face distinct challenges requiring tailored solutions.
Practical strategies to address SUD must include public awareness campaigns, accessible treatment options, and targeted prevention programs. By focusing on these initiatives, we can reduce the overall impact of substance use disorder on individuals, families, and communities.
Conclusion
Substance use disorder is a complex issue that touches every age group, each with its unique challenges. Young adults remain the most affected demographic, but teens and older adults also face significant risks. Understanding these age-specific patterns allows us to create better prevention programs and treatment options tailored to individual needs.
If you or a loved one is struggling with substance use disorder, help is available. Call Virtue Recovery Las Vegas at 866-520-2861 to speak with compassionate professionals who can guide you toward recovery. No matter your age, it’s never too late to start your journey to a healthier, substance-free life.
FAQs About 2023 Drug and Alcohol Substance Abuse Statistics
What Is Substance Use Disorder?
Substance use disorder (SUD) is a medical condition where a person struggles to control their use of drugs or alcohol, leading to health, social, and behavioral issues.
Which Age Group Has the Highest Rate of SUD?
According to 2023 data, the highest prevalence is among adults aged 18–29, with nearly 28% affected.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of SUD?
If left untreated, SUD can lead to chronic health problems, mental health issues, and difficulties in personal and professional relationships.
How Can Families Support Someone with SUD?
Families can help by offering emotional support, encouraging treatment, and participating in family counseling or support groups.
Where Can I Find Treatment for SUD?
Professional addiction recovery programs like Virtue Recovery Las Vegas offer specialized care tailored to each individual’s needs.