Gambling, often seen as a harmless form of entertainment, can spiral into a destructive addiction, creating a dual battle with significant mental health fallout. We delve deep into understanding gambling addiction, its profound impact on mental health, the intertwining risk factors, effective treatment modalities, and crucial prevention strategies.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding Gambling Addiction: A compulsive need to gamble, despite harmful consequences.
- Mental Health Impacts: Links to depression, anxiety, and other mental disorders.
- Risk Factors: Genetic, environmental, and psychological contributors.
- Treatment Approaches: Behavioral therapies and support networks.
- Prevention Strategies: Awareness and early interventions.
I. Understanding Gambling Addiction
Gambling addiction, or pathological gambling, is an intense and persistent urge to gamble, transcending the boundaries of recreational gambling to become an all-consuming obsession with severe life consequences. Those afflicted often get caught in a destructive cycle of chasing losses, continuing to gamble to recoup lost funds, oblivious to the spiraling adverse effects. Unlike casual gamblers, people with gambling addiction center their lives around gambling, constantly preoccupied with the next bet and the pursuit of funds for gambling, driven by an escalating need for greater thrills and stakes. This quest for a bigger rush typically results in increased risks and substantial losses, temporarily masking the reality of consistent losses and the ensuing financial struggles, relationship strains, and mental health deterioration.
Individuals grappling with gambling addiction frequently use gambling as a means of escaping from issues or alleviating distressing emotions like helplessness, guilt, anxiety, or depression. However, the brief respite and excitement provided by gambling are soon eclipsed by long-term detrimental effects, including financial devastation, legal problems, job loss, and familial strife. It’s crucial to understand that gambling addiction is a complex condition rooted in biological, genetic, and environmental factors, and it is often linked with mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and suicidal tendencies.
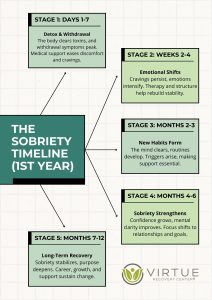
The treatment for gambling addiction involves a multifaceted approach, including therapy, support groups, and, at times, medication. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has proven especially effective in helping individuals alter their destructive gambling behaviors and thought patterns. Moreover, support groups like Gamblers Anonymous offer a supportive community for those facing similar challenges, fostering a sense of solidarity and accountability.
II. Mental Health Impacts
Depression and Anxiety:
- Prevalence: A significant number of gambling addicts experience depression and anxiety.
- Symptoms: Feelings of hopelessness, increased anxiety, and social withdrawal are common.
- Consequences: In severe cases, this can lead to suicidal thoughts and actions.
Depression and anxiety are common comorbidities associated with gambling addiction, often creating a complex interplay that exacerbates both conditions. Individuals struggling with gambling issues frequently exhibit symptoms of depression and anxiety. These include persistent sadness, a lack of interest in activities they once found enjoyable, and an overwhelming sense of worry or fear. This psychological distress can lead to a harmful cycle where gambling becomes a coping mechanism to escape or alleviate negative emotions. Ironically, this behavior often exacerbates these feelings instead of providing relief.
The situation is further complicated by the financial strain, relationship conflicts, and social isolation that often accompany chronic gambling. These factors can deepen depressive states and elevate anxiety levels. Additionally, the biochemical changes in the brain associated with gambling addictions, such as the dysregulation of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, can directly influence mood and anxiety disorders. Addressing these co-occurring mental health issues is critical for the effective treatment and recovery of individuals suffering from gambling addiction.
Other Psychological Disorders:
- Substance Abuse: Co-occurring substance abuse is frequent, with individuals using alcohol or drugs to cope with gambling losses.
- Personality Disorders: There is a higher incidence of personality disorders among gambling addicts.
- Stress and PTSD: The constant stress of gambling debts and lifestyle can lead to symptoms resembling post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Gambling addiction can be intertwined with various other psychological disorders, presenting a multifaceted challenge in mental health. Beyond depression and anxiety, individuals with gambling issues are at an increased risk of developing other disorders, such as bipolar disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). These conditions may either precede the gambling problem or be exacerbated by the compulsive gambling behavior. For instance, the manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder can lead to impulsive and risky decision-making, including excessive gambling. Similarly, the impulsivity and restlessness characteristic of ADHD can contribute to the development of gambling problems. OCD, with its hallmark of repetitive behaviors and thoughts, can manifest in the persistent urge to gamble. These intertwined disorders highlight the importance of a holistic treatment approach that addresses both the gambling addiction and any underlying psychological issues.
III. Risk Factors for Gambling Addiction
- Genetic Predisposition: Genetics play a role, with a higher risk observed in individuals who have a family history of addiction.
- Psychological Factors:
- Impulse Control: Poor impulse control is a significant contributor.
- Reward Sensitivity: Heightened sensitivity to the rewards of gambling can foster addiction.
- Environmental Influences: Exposure to gambling environments or having a social circle that gambles increases risk.
The development of gambling addiction is influenced by a complex interplay of various risk factors. Sociocultural elements play a significant role, including accessibility to gambling venues and societal attitudes towards gambling. Individuals in environments where gambling is readily accessible and culturally normalized are at a higher risk. Additionally, family and peer influences are crucial; growing up in a family where gambling is common or being part of a social circle that frequently gambles can increase the likelihood of developing a gambling problem.
Genetic predisposition is also a factor in the risk of gaming addiction, with research indicating that individuals with a family history of addiction are more prone to gambling addiction. Personal characteristics such as high impulsivity, a preference for high-risk activities, and a history of traumatic experiences or adversity are associated with a greater risk. These factors, combined with potential financial stress or the allure of escaping personal problems through gambling, create a fertile ground for the development of pathological gambling behaviors. Understanding these risk factors is key to developing effective prevention and intervention strategies for those vulnerable to gambling addiction.
IV. Treatment Approaches
Behavioral Therapies:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps in changing harmful gambling behaviors and thoughts, such as rationalizations and false beliefs.
- Motivational Interviewing: This technique enhances an individual’s motivation to change gambling behavior.
- Medication: While no medication specifically treats gambling addiction, those for co-occurring disorders like depression can be beneficial.
Support Networks:
- Group Support: Groups like Gamblers Anonymous provide peer support to help deal with the addiction.
- Family Therapy: Family support is crucial in the recovery process, providing a strong support system.
Treatment for gambling addiction often involves a multifaceted approach tailored to meet the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. One of the most effective treatment modalities is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which helps individuals identify and change unhealthy gambling behaviors and thoughts. CBT focuses on challenging and restructuring cognitive distortions about gambling, such as the belief in a ‘big win’ that is just around the corner. This therapy also equips individuals with strategies to cope with urges to gamble, handle relapse situations, and address problems exacerbated by gambling, like financial, work, or relationship issues.
In addition to psychological therapies, many find support groups like Gamblers Anonymous invaluable. These groups offer peer support and a sense of community, helping individuals feel less isolated. They provide a space for sharing experiences and learning from others who have faced similar challenges. For some, medication can be a helpful part of treatment, particularly if they’re dealing with co-occurring disorders such as depression or anxiety. Medications can alleviate these symptoms, potentially reducing the urge to gamble. Overall, successful treatment of gambling addiction requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the behavioral, psychological, and often financial repercussions of the disorder.
V. Prevention Strategies
- Education and Awareness: Public awareness campaigns about the dangers of gaming addiction.
- Early Intervention: Identifying and intervening in cases of early gambling behaviors.
- Regulation and Policy: Implementing policies that limit the accessibility and attractiveness of gambling.
Educational programs play a crucial role in preventing gaming addiction, particularly among those most at risk. These programs are designed to demystify the often glamourized image of gambling portrayed in media and advertising, providing a realistic picture of the risks involved. They should focus on raising awareness about the signs of problem gambling and emphasize the importance of early intervention. By fostering a deeper understanding of gambling, individuals can make more informed choices about participating in such activities.
Implementing responsible gambling practices in casinos and other betting venues is also a key preventive strategy. Measures such as setting limits on the amounts and time spent gambling, offering resources for self-exclusion programs, and training staff to recognize and assist those showing signs of problem gambling can greatly mitigate risks. Additionally, individuals can benefit from engaging in healthy alternative activities or hobbies, offering positive outlets for stress and recreation. These alternatives reduce the reliance on gambling as a primary source of entertainment or escapism.
Conclusion
The battle against gaming addiction and its mental health repercussions is multifaceted, requiring a comprehensive approach encompassing understanding, treatment, and prevention. By addressing both the addiction and its accompanying mental health issues, individuals can find the path to recovery and regain control over their lives.
Have a loved one who is struggling with substance use disorder or gambling addiction? Let Virtue Recovery Centers help. We are a leading provider of many treatment programs tailored to help with a myriad of addict treatment and mental health services. Reach out to an admissions counselor TODAY to get more information about our treatment programs. Begin the help you or your loved ones needs today.
FAQ Section:
Q1: What is the primary cause of gambling addiction?
A1: Gambling addiction is caused by a combination of genetic, psychological, and environmental factors.
Q2: How does gambling addiction affect mental health?
A2: It can lead to depression, anxiety, stress, and, in severe cases, suicidal thoughts.
Q3: Can gambling addiction be treated with medication?
A3: There’s no specific medication for gambling addiction, but medications for co-occurring disorders can be helpful.
Q4: What role does family play in treating gambling addiction?
A4: Family support is crucial in recovery, offering emotional support and helping to rebuild trust.
Q5: How can gambling addiction be prevented?
A5: Prevention strategies include education, early interventions, and regulatory policies to limit gambling accessibility. Gambling, often seen as a harmless form of entertainment, can spiral into a destructive addiction, creating a dual battle with significant mental health fallout. This article delves deep into understanding gambling addiction, its profound impact on mental health, the intertwining risk factors, effective treatment modalities, and crucial prevention strategies.
Citations
This article references the following sources:
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
- Petry, N. M. (2005). Pathological Gambling: Etiology, Comorbidity, and Treatment. American Psychological Association.
- Grant, J. E., & Potenza, M. N. (2004). Pathological Gambling: A Clinical Guide to Treatment. American Psychiatric Pub.
- Shaffer, H. J., & Martin, R. (2011). Disordered Gambling: Etiology, Trajectory, and Clinical Considerations. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 7, 483-510.
- National Council on Problem Gambling. (2021). Problem Gambling Awareness and Resources. Retrieved from https://www.ncpgambling.org/
- American Psychological Association. (2020). Understanding the Psychology of Gambling. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/
- Gamblers Anonymous. (2021). About the Recovery Program. Retrieved from https://www.gamblersanonymous.org/
- Ledgerwood, D. M., & Petry, N. M. (2006). Psychological Experience of Gambling and Subclinical Pathological Gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 22(3), 235-245.
- Blaszczynski, A., & Nower, L. (2002). A pathways model of problem and pathological gambling. Addiction, 97(5), 487-499.
- Kessler, R. C., Hwang, I., LaBrie, R., Petukhova, M., Sampson, N. A., Winters, K. C., & Shaffer, H. J. (2008). DSM-IV pathological gambling in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Psychological Medicine, 38(9), 1351-1360.