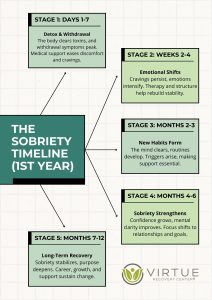
Summary
Stigma significantly impacts LGBTQIA+ individuals dealing with substance abuse. It leads to mental health issues and higher rates of substance use disorders. Discrimination, internalized stigma, and lack of culturally competent care are key factors. Addressing these challenges through supportive environments and tailored treatment is crucial for improving outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding Stigma and Its Effects – How stigma impacts mental health and substance use.
- Minority Stress Model – Explaining the minority stress model and its contribution to substance abuse.
- Statistics Highlighting the Problem – Key statistics on substance use in the LGBTQIA+ community.
- Factors Contributing to Substance Abuse – Discrimination, internalized stigma, and lack of social support.
- Implications for Treatment – Barriers to seeking help, the importance of culturally competent care, and recommendations for improving treatment outcomes.
Introduction
Substance use disorder is a significant issue within the LGBTQIA+ community, exacerbated by the stigma and discrimination these individuals often face. Understanding the impact of stigma on LGBTQIA+ substance abuse is crucial for developing effective treatment and support systems. Virtue Recovery Las Vegas is dedicated to providing compassionate and culturally competent care for LGBTQIA+ individuals struggling with addiction.
Understanding Stigma and Its Effects
Stigma, in the context of substance use disorder and the LGBTQIA+ community, refers to the negative attitudes and beliefs that society holds about both addiction and non-heteronormative identities. This stigma manifests in various forms, including discrimination, social rejection, and internalized homophobia or transphobia. The impact of stigma on mental health is profound, often leading to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem, which can drive individuals to substance use as a coping mechanism.
Minority Stress Model
The minority stress model explains how minority stress, arising from a hostile and stressful social environment, contributes to health disparities. For LGBTQIA+ individuals, the stress associated with their sexual orientation and gender identity can lead to higher levels of substance abuse. This model highlights the chronic stress from discrimination, prejudice, and internalized stigma, all of which elevate the risk of developing substance use disorders.
Statistics Highlighting the Problem
Data from the National Institute on Drug Abuse shows that 41.3% of LGBTQIA+ adults reported using marijuana in the past year, compared to 18.7% of the overall population. Similarly, 21.8% had an alcohol use disorder, compared to 11.0% of the general population. Furthermore, the National Drug Strategy Household Survey found nearly 47% of gay, lesbian, or bisexual individuals used illicit drugs in the past 12 months, significantly higher than their heterosexual peers. These statistics underscore the disparity in substance use between LGBTQIA+ individuals and the general population.
Factors Contributing to Substance Abuse
Discrimination and Harassment
Discrimination and harassment are significant factors contributing to substance abuse among LGBTQIA+ individuals. Experiences of prejudice and violence can lead to substance use as a coping mechanism. The fear of rejection and actual instances of discrimination in various settings, including workplaces and healthcare, exacerbate these issues.
Internalized Stigma and Mental Health
Internalized stigma refers to the process by which LGBTQIA+ individuals accept society’s negative perceptions and apply them to themselves. This can result in internalized homophobia or transphobia, leading to mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and low self-worth. These mental health challenges often drive individuals to substance use as a means of coping.
Lack of Social Support
The lack of adequate social support networks further contributes to the high rates of substance abuse in the LGBTQIA+ community. Social support is crucial for emotional well-being, and its absence can lead individuals to seek solace in drugs or alcohol.
Implications for Treatment
Barriers to Seeking Help
Stigma and discrimination in healthcare settings deter LGBTQIA+ individuals from seeking help for substance use disorders. Fear of prejudice and lack of understanding among healthcare providers often results in untreated disorders and more severe addiction issues by the time treatment is sought.
Importance of Culturally Competent Care
Culturally competent care is essential for effective treatment of substance use disorders in the LGBTQIA+ community. Healthcare providers must be trained to understand the unique challenges faced by LGBTQIA+ individuals and to offer nonjudgmental, supportive care.
Recommendations for Improving Treatment Outcomes
- Enhanced Training: Healthcare providers should receive training on LGBTQIA+ issues and cultural competence.
- Supportive Environments: Create safe and inclusive spaces within treatment centers.
- Community Involvement: Engage LGBTQIA+ communities in developing and implementing treatment programs to ensure they meet the specific needs of these populations.
Conclusion
The impact of stigma on substance abuse in the LGBTQIA+ community is profound, leading to higher rates of addiction and significant barriers to seeking treatment. Understanding and addressing these challenges through culturally competent care and supportive environments is crucial for improving treatment outcomes. Virtue Recovery Las Vegas is committed to providing the necessary support for LGBTQIA+ individuals struggling with addiction. For compassionate and effective care, contact us at 866-520-2861.
FAQs
How does stigma impact substance use disorder in the LGBTQIA+ community?
Stigma leads to mental health issues like anxiety and depression, which can drive substance use as a coping mechanism.
What is the minority stress model?
The minority stress model explains how chronic stress from discrimination and prejudice contributes to health disparities, including higher rates of substance use.
Why is culturally competent care important for treating substance use in LGBTQIA+ individuals?
Culturally competent care ensures that treatment addresses the unique challenges faced by LGBTQIA+ individuals, leading to better outcomes.
What are the barriers to seeking help for substance use disorders in the LGBTQIA+ community?
Barriers include fear of discrimination, lack of culturally competent care, and past negative experiences with healthcare providers.
How to reduce the stigma of LGBTQIA+?
Reducing the stigma of LGBTQIA+ individuals involves education, promoting inclusivity, and fostering empathy. Encouraging open dialogue, challenging stereotypes, and supporting anti-discrimination policies can help create a more accepting society.
What are the mental health issues with LGBTQ?
LGBTQ individuals often face higher rates of anxiety, depression, and substance abuse due to societal stigma, discrimination, and rejection. They may also experience unique stressors related to their sexual orientation or gender identity, such as internalized homophobia or transphobia, and difficulties in coming out.
What are the five barriers to mental health promotion?
The five barriers to mental health promotion include lack of awareness and education about mental health issues, stigma and discrimination associated with mental illness, limited access to mental health services, cultural and language barriers, and socioeconomic factors that affect one’s ability to seek and receive adequate care.
How can treatment outcomes be improved for LGBTQIA+ individuals with substance use disorders?
Improving treatment outcomes involves training healthcare providers, creating supportive environments, and engaging the LGBTQIA+ community in program development.
Resources
https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/lgbtqi-people-and-substance-use
https://www.sojournerhousepa.org/substance-use-disorders-impact-on-the-lgbtqia-community/
https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/lgbtiq-communities/lgbt-people-alcohol-drugs
https://news.cornell.edu/stories/2019/12/discrimination-impacts-health-lgbt-people-analysis-finds
https://substanceabusepolicy.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13011-023-00581-8